The Moneyball Moment for Security: How VLMs and MCPs Will Reshape Security Services
Unlocking the $400B Security Operations & $400B MSSP Market with AI That Actually Sees and Understands at Scale
The Moneyball Moment for Security: How VLMs and MCPs Will Reshape Security Services
In the 2011 film Moneyball, we witness a pivotal shift in baseball management. The Oakland Athletics, led by Billy Beane (played by Brad Pitt), revolutionize their approach by replacing subjective scouting judgments with data-driven player analysis. This transformation allowed a team with limited resources to compete against wealthier organizations by identifying undervalued talent through statistical methods rather than traditional intuition.
Today's security industry stands at a similar inflection point. For decades, security teams have relied heavily on human expertise and intuition to detect and respond to threats. Despite investments in automation tools, the field remains overwhelmingly dependent on skilled analysts making judgment calls—much like baseball's dependence on human scouts before the Moneyball revolution.
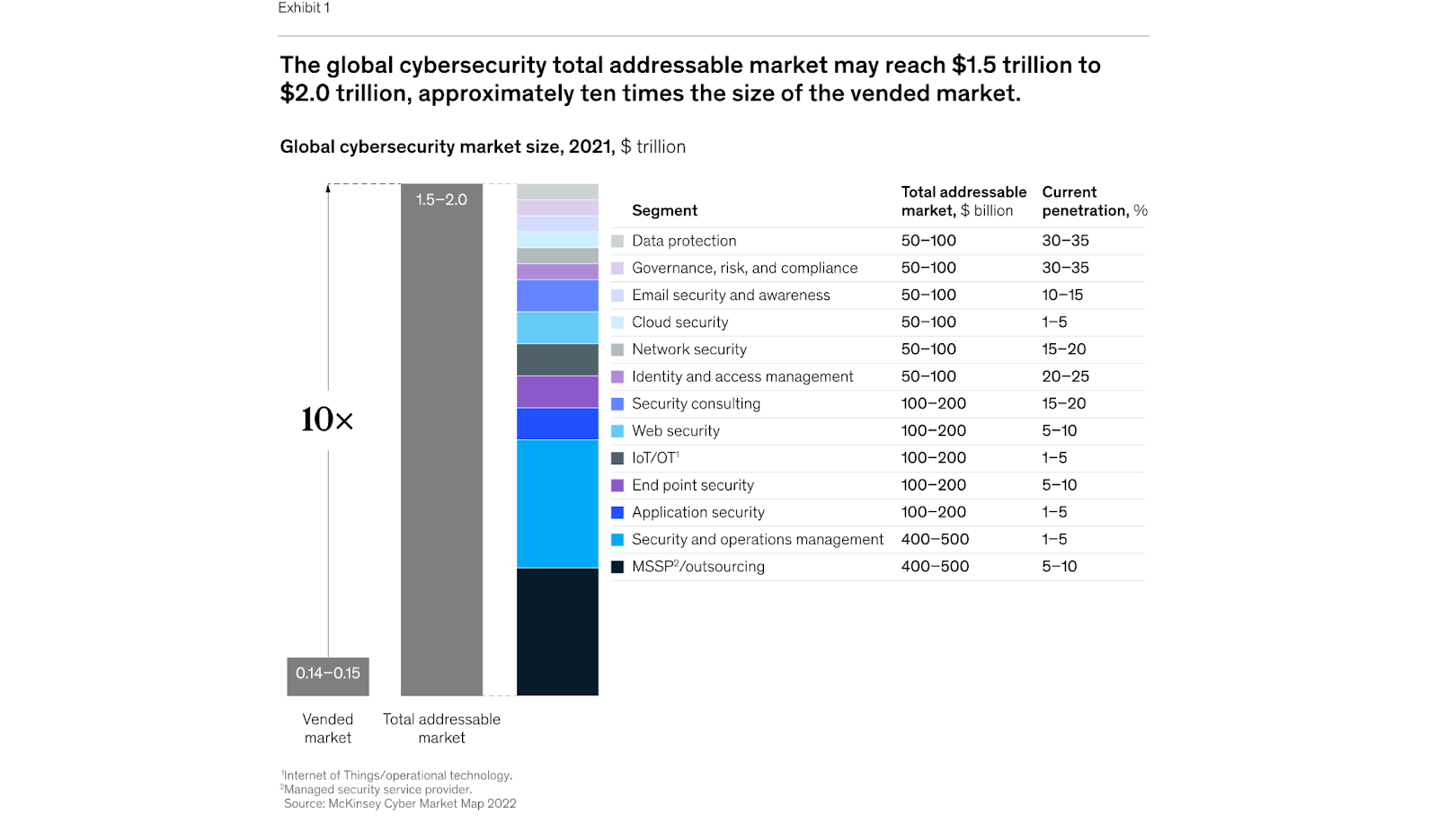
This transformation couldn't come at a more critical time. According to McKinsey research, the global cybersecurity addressable market is projected to reach $1.5-2.0 trillion, approximately ten times the size of the current vended market of roughly $150 billion. Most notably, the Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) outsourcing and security operations management segments represent the largest individual opportunities—each with a $400-500 billion addressable market and remarkably low current penetration rates of just 1-10%. Together, these two segments account for nearly half of the entire cybersecurity market potential, highlighting the massive opportunity for innovation in security services delivery.
The convergence of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) represents security's "Moneyball moment"—a fundamental shift from human-centric operations to AI-driven approaches that can see, understand, and orchestrate complex security workflows with unprecedented efficiency and effectiveness.
Just as the Athletics' data-driven approach changed baseball forever, the integration of VLMs and Anthropic's MCP is poised to transform how security services operate, moving from labor-intensive processes to intelligence-driven automation that can handle the cognitive complexity of security decision-making at scale—potentially unlocking billions in value across the vastly underpenetrated MSSP and security operations markets.
The Automation Paradox in Security Operations
Despite significant investments in automation technologies, security teams today find themselves in a paradoxical situation: they're drowning in tools yet starving for results. The statistics tell a compelling story of this disconnect:
According to IBM's 2023 Cost of a Data Breach Report, organizations with fully deployed security automation saved an average of $3.05 million per breach compared to those without automation—yet only 31% of organizations have fully deployed security automation1. This gap exists because current automation approaches are fundamentally mismatched to security's dynamic challenges.
The average enterprise security team faces approximately 11,000 alerts daily, of which around 70% go uninvestigated due to resource constraints2. Traditional automation tools like SOAR (Security Orchestration, Automation and Response) platforms and RPA (Robotic Process Automation) solutions promised to address this volume crisis but have fallen short in three critical ways:
First, they operate primarily on structured data and predefined patterns, yet modern threats thrive in unstructured, visual, and constantly evolving environments. When Gartner surveyed security leaders who had implemented SOAR solutions, 67% reported that maintaining playbooks and integrations required significantly more resources than anticipated3.
Second, traditional automation excels at repetitive tasks but struggles with the cognitive complexity of security decisions. Security analysts must constantly synthesize information across disparate systems, interpret visual data from dashboards and interfaces, and make judgment calls based on incomplete information—capabilities that script-based automation simply cannot replicate.
Third, the economics of conventional automation become increasingly unfavorable in security contexts. A study by Ponemon Institute found that security teams spend an average of 26% of their time maintaining security automation scripts and playbooks rather than actively hunting threats4. This maintenance burden increases as threats evolve, creating a negative ROI spiral where more resources are consumed by the automation tools themselves than are saved by their operation.
The fundamental limitation lies in trying to automate security operations using technologies designed for stable, predictable environments. Security is inherently dynamic, visual, and contextual—qualities that traditional automation frameworks were never designed to handle. As one CISO aptly put it: "We've spent millions automating the easy 20% of security operations while the hard 80% still requires human analysts."
This is precisely where the convergence of Vision-Language Models and Anthropic's Model Context Protocol enters the picture, offering a fundamentally different approach to security automation that addresses these longstanding limitations.
The Visual Revolution: How VLMs Are Changing the Game
Enter Vision-Language Models (VLMs), which represent a paradigm shift in automation capabilities that directly address the limitations of traditional approaches. Unlike conventional automation tools that rely on structured data and predefined pathways, VLMs can "see" and interpret interfaces much like human analysts do.
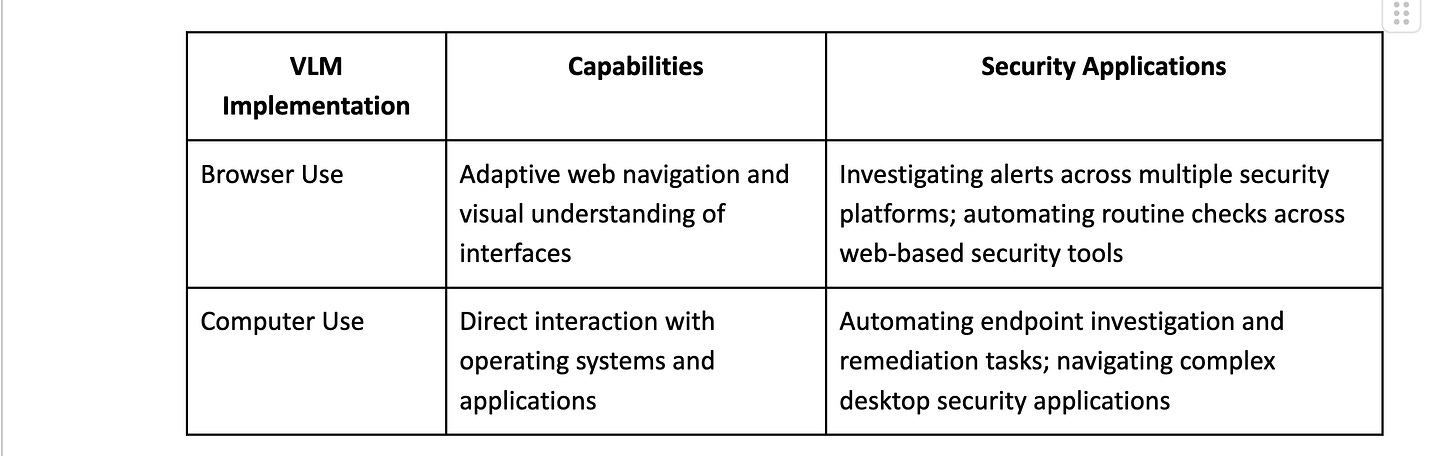
VLMs combine computer vision with natural language understanding to interpret what's happening on screens, dashboards, and applications. At a practical level, they work by tokenizing images into discrete visual elements that can be processed alongside text, with tools like Browser Use adding preprocessing layers to create effective browser automation APIs. This visual cognition capability means they can work with security interfaces exactly as they are—without requiring custom APIs, specialized integrations, or brittle screen-scraping scripts.
The implications for security operations are profound. Consider that 84% of security analysts report spending significant time navigating between different tools and interfaces during investigations[^5]. This interface-hopping creates significant inefficiencies and increases the risk of missing critical information. VLMs can dramatically reduce this burden by observing these same interfaces, understanding their context, and interacting with them directly—essentially automating what was previously thought to require human visual cognition.
This capability is especially valuable for resource-constrained security teams that can't afford specialized integration efforts. To make VLM adoption practical for these teams, the open-source community has developed several lightweight models that balance performance with deployability.
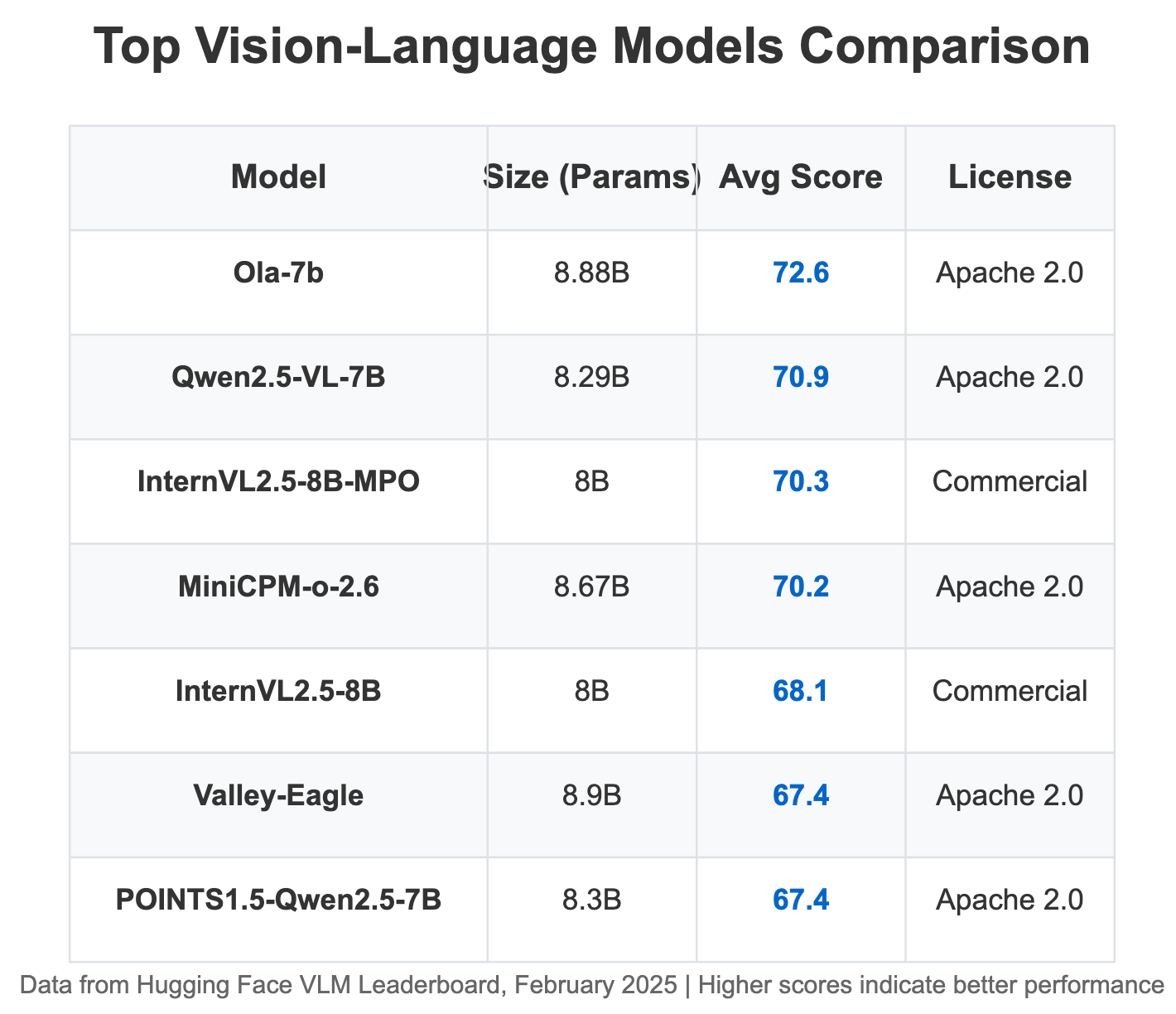
Lightweight Open-Source VLMs: Balancing Performance and Deployability
For enterprises prioritizing efficient deployment alongside solid performance, several open-source VLMs with reasonable parameter counts offer impressive capabilities: These models provide practical deployment options for security teams seeking to leverage visual automation without massive
infrastructure investments. Their open-source licensing (with the exception of InternVL) also enables customization for specific security use cases and integration with existing security tools.
Several breakthrough implementations are already demonstrating this potential:
These tools represent a fundamental shift from traditional automation in three key ways:
First, they're adaptable. When security interfaces change—as they frequently do with updates—VLMs can adjust without requiring reprogramming. Research indicates VLMs can maintain effectiveness after significant UI changes that would completely break traditional RPA scripts.
Second, they're contextual. VLMs excel at identifying interface elements like alerts, dashboards, and visual indicators across security platforms. They can recognize severity indicators (like red alerts vs. yellow warnings), locate key information on complex security interfaces, and extract relevant data points from visualizations. When paired with specialized security language models through MCP orchestration, this visual understanding becomes even more powerful—the VLM handles the "seeing" while security-focused reasoning models analyze the extracted information, creating a system that combines visual navigation with domain-specific security expertise.
Third, they're composable. VLMs can be combined with other AI capabilities to create end-to-end workflows. For example, a VLM can navigate a SIEM dashboard and extract alert data, which is then fed into a specialized language model (SLMs) for domain-specific analysis. This creates a powerful chain where the VLM handles visual interaction and data extraction, while the specialized security model—trained specifically on threat intelligence, attack patterns, and security protocols—provides focused analytical capabilities without the overhead of a general-purpose model
The ability to deploy these compact models on-premises addresses key security concerns for enterprise security teams, particularly around data confidentiality and compliance requirements. With lightweight open-source alternatives performing at increasingly competitive levels, security teams can now leverage visual automation without sacrificing control over their sensitive security data or requiring massive infrastructure investments.
While VLMs excel at interface interaction, they need a strategic layer to orchestrate complex security workflows across multiple systems and decision points. This is where Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) enters the picture.
Beyond Single Actions: The MCP Orchestration Layer
Vision-Language Models provide remarkable capabilities for interacting with interfaces, but security operations require more than just isolated actions—they demand coordinated workflows that can reason across multiple systems, adapt to changing conditions, and make strategic decisions. This is where Anthropic's Model Context Protocol (MCP) transforms the automation landscape.
Understanding Model Context Protocol
Model Context Protocol is an innovative approach that creates a standardized communication layer between AI models and computer applications. Unlike traditional APIs that require specific programming for each application, MCP establishes a universal interface that works across different systems. This allows AI models to control both:
Applications with existing APIs, but with greater flexibility and natural language interaction
Applications without APIs, using visual interface navigation through VLM capabilities
The true power of MCP lies in its ability to maintain context and orchestrate complex, multi-step processes across disparate systems—precisely what security operations require.
MCP Architecture: Servers and Clients
The MCP ecosystem consists of two primary components:
MCP Servers act as the orchestration layer that maintains state, manages context, and coordinates the execution of complex workflows. These servers can process natural language instructions and translate them into coordinated actions across multiple systems.
MCP Clients are the interfaces to specific applications or systems. These can leverage APIs when available or use visual interaction through VLMs when direct API access isn't possible.
Several implementations of MCP servers are emerging, such as Composio https://mcp.so/servers which lists over 1900 MCP servers (
https://mcp.composio.dev/
), which provides a platform for building, testing, and deploying MCP-based workflows. These platforms enable security teams to create sophisticated automation scenarios without extensive programming knowledge.
Adaptive Reasoning in Security Operations
What makes MCP particularly valuable for security operations is its standardized communication framework. MCP serves as an API wrapper layer that enables LLM-based agentic systems to interact seamlessly with applications. While MCP itself doesn't perform reasoning, it creates the foundation for LLM agentic systems to orchestrate complex security workflows, adapting their approach based on findings and making informed decisions across different security tools and interfaces - capabilities that traditional automation frameworks weren't designed to support. With MCP we can:
Process ambiguous security alerts and determine appropriate investigation paths
Adapt workflows in real-time based on findings during an investigation
Handle exception cases that would normally require human intervention
For example, when investigating a potential data exfiltration alert, an MCP-orchestrated workflow might:
First examine the alert details in a SIEM dashboard
Cross-reference the affected user's recent activities in an identity management system
Check endpoint logs for unusual behaviors
Analyze network traffic patterns for confirmation
Dynamically adjust the investigation based on findings at each step
This type of adaptive workflow would traditionally require a security analyst manually piecing together information across multiple systems—a process that could take hours. With MCP orchestration, it can happen in minutes with minimal human involvement.
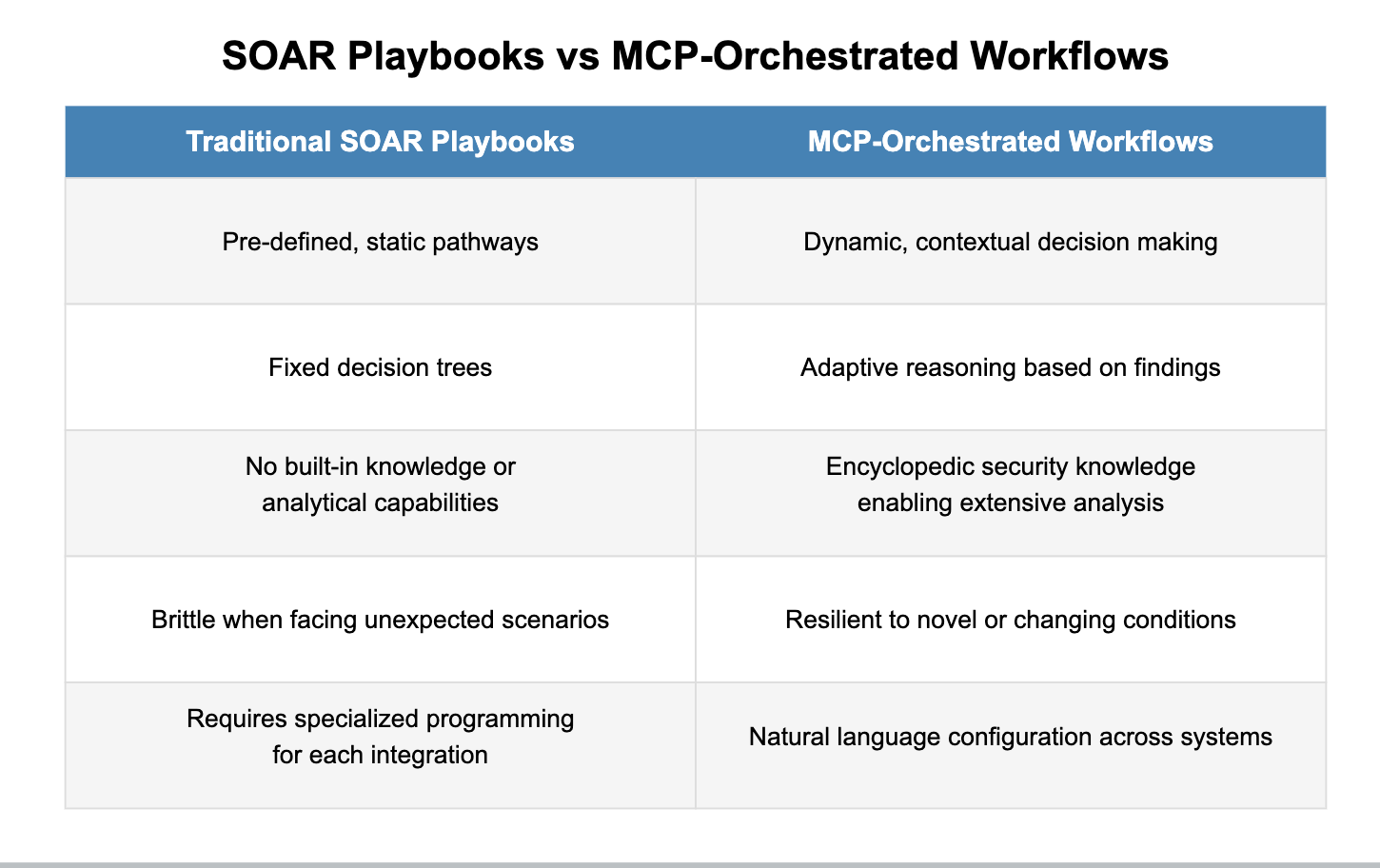
From Rigid Playbooks to Strategic Coordination
The transition from traditional SOAR playbooks to MCP-orchestrated workflows represents a fundamental evolution in security automation:
This shift enables security teams to automate far more complex scenarios than previously possible. Rather than automating only the simplest 20% of security tasks, organizations can now address the cognitive complexity of the remaining 80%—dramatically increasing operational efficiency.
By combining VLMs' visual interaction capabilities with MCP's orchestration power, security operations can enter a new era of automation that more closely resembles human analyst workflows while operating at machine scale and speed.
The Power of Convergence: VLMs + MCPs as the Complete Solution
While VLMs and MCP each bring powerful capabilities independently, their true transformative potential emerges when they're combined into a unified solution. This convergence creates end-to-end automation possibilities that were previously unthinkable in security operations.
End-to-End Automation: From Alert Detection to Resolution
The integration of VLMs and MCP enables complete automation cycles that can:
Detect security anomalies across multiple monitoring systems
Investigate alerts by gathering and correlating evidence from diverse sources
Analyze the severity and context of potential threats
Respond with appropriate containment or remediation actions
Document the entire incident lifecycle for compliance and learning
This comprehensive approach addresses the fundamental challenge that has limited security automation adoption: the inability to handle the full complexity of security operations without constant human intervention.
Transformative Use Cases
The combined power of VLMs and MCP is already enabling several high-impact security use cases:
✅ Real-time Threat Detection & Response
VLM Role
Visually navigate security dashboards to examine alert details
Interpret complex security visualizations showing attack patterns
Extract relevant data from security tools without pre-built integrations
Interact with endpoint management consoles to gather system information
MCP Role
Coordinate the overall investigation workflow
Maintain context about the incident across multiple systems
Make logical decisions about threat severity and appropriate response
Trigger automated containment protocols based on threat assessment
These complementary capabilities reduce response times from hours to minutes, significantly limiting potential damage from active threats.
✅ Automated Compliance Enforcement
VLM Role
Visually scan configuration screens across multiple systems
Identify non-compliant settings through visual interface analysis
Navigate complex GRC (Governance, Risk, Compliance) platforms
Capture screenshots and evidence for audit documentation
MCP Role
Track compliance requirements and map them to specific controls
Orchestrate remediation workflows across different compliance domains
Maintain audit trails of compliance activities and generate reports
Adapt compliance checking based on regulatory changes
Organizations can maintain continuous compliance rather than scrambling during audit cycles, reducing both risk and operational overhead.
✅ Improved Phishing & Fraud Defense
VLM Role
Visually analyze reported phishing emails, including images and formatting
Examine suspicious login pages and website content
Navigate email security consoles to quarantine threats
Interact with threat intelligence platforms through their interfaces
MCP Role
Coordinate multi-stage analysis across threat intelligence sources
Track patterns across multiple phishing attempts to identify campaigns
Orchestrate user communication and credential reset workflows
Maintain context on evolving phishing tactics and adjust detection strategies
✅ Faster SOC Workflows
VLM Role
Navigate between various security consoles and dashboards
Extract relevant data from alerts across different security tools
Interact with ticketing systems to update case information
Generate visual reports and evidence documentation
MCP Role
Coordinate parallel investigation streams across multiple tools
Prioritize incidents based on comprehensive risk assessment
Maintain investigation context and track analyst handoffs
Apply security playbooks with adaptive decision-making
✅ Stronger Zero-Trust Security
VLM Role
Monitor behavior across user interfaces to detect anomalies
Interpret identity management dashboards and access controls
Navigate IAM consoles to adjust permissions when needed
Interact with endpoint security tools to verify device compliance
MCP Role
Coordinate continuous verification across authentication systems
Track risk scores and contextual factors for access decisions
Orchestrate step-up authentication workflows based on risk assessment
Maintain a holistic view of identity, device, and network trust signals
Agentic Tools: Tying Everything Together
The emerging ecosystem of agentic frameworks is accelerating VLM+MCP adoption. Tools like CrewAI and Langchain provide development frameworks that simplify integration:
CrewAI enables the creation of multi-agent systems where specialized AI agents collaborate on complex security tasks
Langchain provides composable components for building sophisticated reasoning workflows
These frameworks are reducing implementation barriers, allowing security teams to leverage VLM+MCP capabilities without extensive AI expertise.
Risks and Challenges
While the potential is tremendous, organizations should be aware of several challenges:
Rapidly Evolving Ecosystem: The technology landscape is changing quickly, with new capabilities and best practices emerging monthly.
Integration Complexity: Connecting these technologies to existing security infrastructure requires careful planning and expertise.
Trust and Verification: Organizations must implement appropriate governance and oversight for AI-driven security decisions. LLM identity is still an unsolved problem.
Skills Gap: Security teams need training to effectively collaborate with and supervise these new automated systems.
Despite these challenges, the convergence of VLMs and MCP represents a fundamental shift in security operations—one that directly addresses the limitations of previous automation approaches. Organizations that successfully navigate this transition will gain significant competitive advantages in both security effectiveness and operational efficiency.
Conclusion: Security's Moneyball Moment
Just as the Oakland Athletics transformed baseball by embracing data-driven decision-making, the security industry now faces its own defining moment. The convergence of VLMs and MCP addresses the fundamental limitations that have constrained traditional security automation.
With a $400-500 billion addressable market for security operations and MSSP services but only 1-10% current penetration, the opportunity is enormous. Organizations that embrace this convergence will gain critical advantages: faster threat response, more comprehensive coverage, reduced costs, and enhanced resilience—all without proportional headcount growth.
The security industry has long sought to "do more with less." The combination of VLMs and MCP finally makes this possible by enabling true cognitive automation that can handle the complexity of security operations at scale.
As with any transformation, early adopters will gain the greatest advantages. The future of security services isn't just about better tools—it's about a fundamentally different approach to solving security's most persistent challenges. That future has arrived, and it will belong to those who recognize and act on security's Moneyball moment.
References
ESG Research, Security Operations Challenges, 2022